Hybrid drives vs mechanical drives

Hybrid hard drives have some of the performance of a solid state drive ( SSD ) with the storage space of a mechanical drive at a much lower cost over SSD. They're bigger than an SSD and faster than a standard hard drive and are sometimes called SSHDs for solid state hybrid drives. Think of s SSHD as a regular hard drive with a lot more cache than the standard 8mb to 64mb cache. The principle is the same except cache is measure in gigabytes as opposed to megabytes.
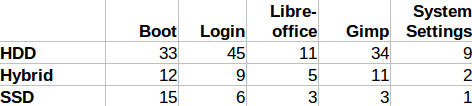
From price per storage capacity standpoint, SSHDs is a compromise between the cost per GB storage vs speed of the drive. Hybrid drives exists because solid state drives are a lot more expensive per GB. Hybrid drives are cheaper than solid state drives because they have a smaller solid-state memory. A 2 TB hybrid drive with 8 GB of solid state cache memory will be more expensive than a simple 2 TB mechanical drive, but magnitudes less expensive than a 2 solid-state drive.
Hybrid drives starts out slow and gets faster as the caching algorithm learns which files should be cached. Initially, a hybrid drive will be no faster than a mechanical drive. With continued use, however, a hybrid drive learns which files should be cached, speed will improve. Having both a solid state drive and a mechanical drive in your system will be faster than a single hybrid drive but with the two drive system, the user will have to manage where the files gets placed. A hybrid drive, on the other hand, the caching algorithm handles what files gets placed where and will change the location of the files as it sees fit. Another advantage of a hybrid drive as opposed to a two drive system is that there may not be any room for a second drive such as in most laptops. Another big advantage is if you have a laptop with a single drive bay; you can get a faster performance without the huge expense of a SSD drive.
Hybrid drives tend to be more reliable than plain old mechanical drives but still has the downside of moving parts wearing with use. The large cache in hybrid drives lends itself to having less fragmentation. The algorithm will write to the largest contiguous space on the physical platter. This has two main benefits, the drive motor won't have to change speed as often and the read / write heads won't have to change position as often. Since hybrid drives cache larger files, the drive motor won't have to ramp up it's speed all of a sudden when a file read or write request is sent. All of this leads to less wear and tear than traditional mechanical drives.